Flashpoint’s VulnDB documents over 400,000 vulnerabilities and has over 5,100 entries in Flashpoint’s KEV database, making it a critical resource as vulnerability exploitation rises. However, if your organization is relying solely on CVE data, you may be missing critical vulnerability metadata and insights that hinder timely remediation. That’s why we created this weekly series—where we surface and analyze the most high priority vulnerabilities security teams need to know about.
Key Vulnerabilities:
Week of June 21 – June 27, 2025
Foundational Prioritization
Of the vulnerabilities Flashpoint published this week, there are 50 that you can take immediate action on. They each have a solution, a public exploit exists, and are remotely exploitable. As such, these vulnerabilities are a great place to begin your prioritization efforts.
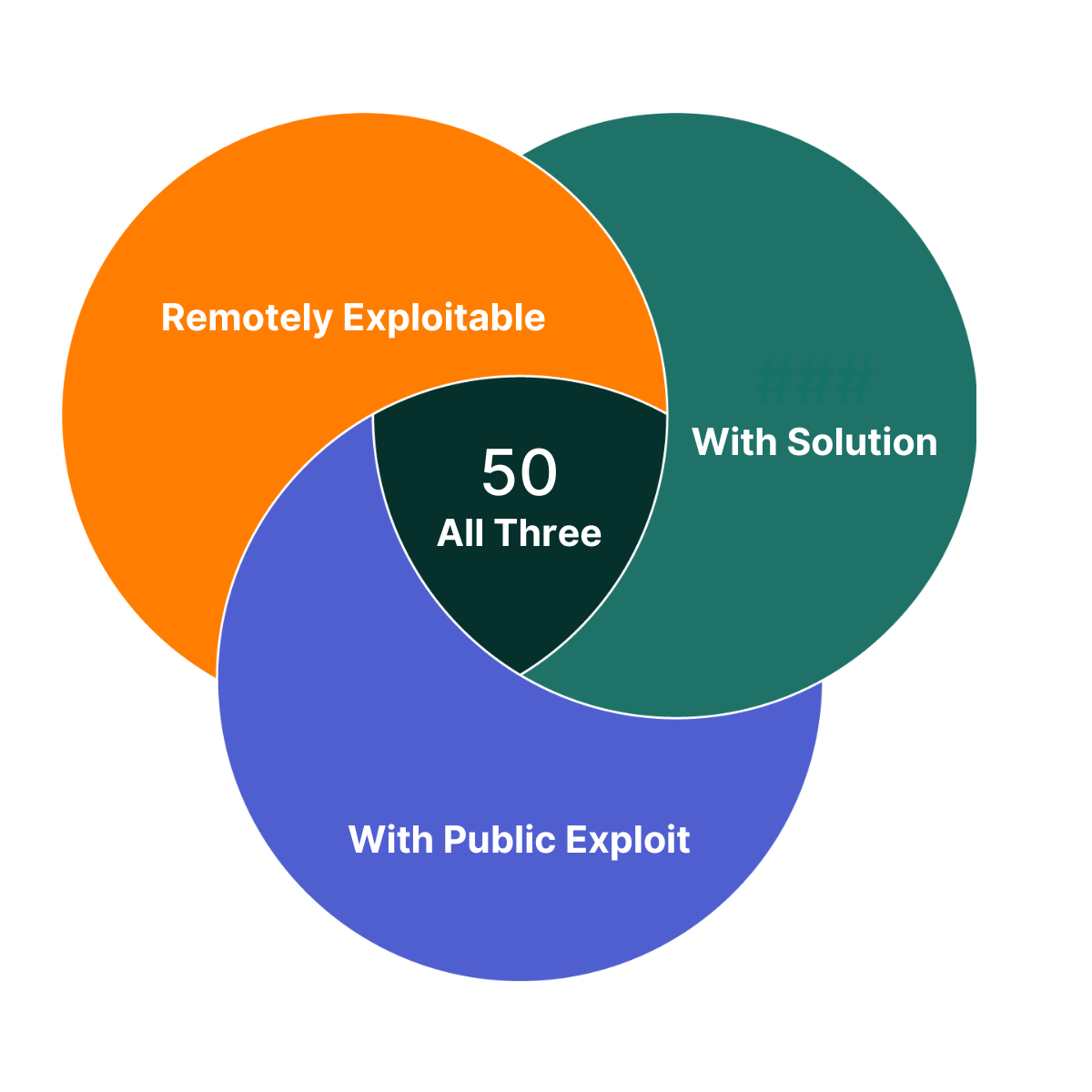
Diving Deeper – Urgent Vulnerabilities
Of the vulnerabilities Flashpoint published last week, five are highlighted in this week’s Vulnerability Insights and Prioritization Report because they contain one or more of the following criteria:
- Are in widely used products and are potentially enterprise-affecting
- Are exploited in the wild or have exploits available
- Allow full system compromise
- Can be exploited via the network alone or in combination with other vulnerabilities
- Have a solution to take action on
In addition, all of these vulnerabilities are easily discoverable and therefore should be investigated and fixed immediately.
To proactively address these vulnerabilities and ensure comprehensive coverage beyond publicly available sources on an ongoing basis, organizations can leverage Flashpoint Vulnerability Intelligence. Flashpoint provides comprehensive coverage encompassing IT, OT, IoT, CoTs, and open-source libraries and dependencies. It catalogs over 100,000 vulnerabilities that are not included in the NVD or lack a CVE ID, ensuring thorough coverage beyond publicly available sources. The vulnerabilities that are not covered by the NVD do not yet have CVE ID assigned and will be noted with a VulnDB ID.
| CVE ID | Title | CVSS Scores (v2, v3, v4) | Exploit Status | Exploit Consequence | Ransomware Likelihood Score | Social Risk Score | Solution Availability |
| CVE-2025-6543 | Citrix NetScaler ADC / Gateway Unspecified Remote Buffer Overflow | 7.6 9.0 9.2 | Exploited in the Wild | Arbitrary Code Execution | Critical | N/A | Yes |
| CVE-2025-3699 | Mitsubishi Electric Multiple Air Conditioners Unspecified Remote Authentication Bypass | 10.0 9.8 9.3 | Private | Remote Authentication Bypass | Medium | N/A | No |
| CVE-2025-34046 | E-office OA (E-office OA自助平台) /general/index/UploadFile.php File Upload Remote Code Execution | 10.0 10.0 10.0 | Exploited in the Wild | Arbitrary Code Execution | Medium | N/A | Yes |
| CVE-2025-34036 | Shenzhen TVT CCTV-DVR /language/<lang> URI Path Handling Remote Command Injection | 10.0 10.0 10.0 | Exploited in the Wild | Arbitrary Command Execution | Medium | N/A | No |
| CVE-2025-34044 | WIFISKY 7-Layer Flow Control Router (WIFISKY 7层流控路由器) confirm.php t Parameter Remote OS Command Execution | 9.0 9.9 9.4 | Exploited in the Wild | Arbitrary Command Execution | Medium | N/A | No |
NOTES: The severity of a given vulnerability score can change whenever new information becomes available. Flashpoint maintains its vulnerability database with the most recent and relevant information available. Login to view more vulnerability metadata and for the most up-to-date information.
CVSS scores: Our analysts calculate, and if needed, adjust NVD’s original CVSS scores based on new information being available.
Social Risk Score: Flashpoint estimates how much attention a vulnerability receives on social media. Increased mentions and discussions elevate the Social Risk Score, indicating a higher likelihood of exploitation. The score considers factors like post volume and authors, and decreases as the vulnerability’s relevance diminishes.
Ransomware Likelihood: This score is a rating that estimates the similarity between a vulnerability and those known to be used in ransomware attacks. As we learn more information about a vulnerability (e.g. exploitation method, technology affected) and uncover additional vulnerabilities used in ransomware attacks, this rating can change.
Flashpoint Ignite lays all of these components out. Below is an example of what this vulnerability record for CVE-2025-6543 looks like.

This record provides additional metadata like affected product versions, MITRE ATT&CK mapping, analyst notes, solution description, classifications, vulnerability timeline and exposure metrics, exploit references and more.
Analyst Comments on the Notable Vulnerabilities
Below, Flashpoint analysts describe the five vulnerabilities highlighted above as vulnerabilities that should be of focus for remediation if your organization is exposed.
CVE-2025-6543
Citrix NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway contain an unspecified overflow condition triggered when certain input is not properly validated. This may allow a remote attacker to cause a buffer overflow, resulting in a denial of service or potentially allowing the execution of arbitrary code. As of June 25, this has been reported as being exploited in the wild. The vendor reports that NetScaler must be configured as Gateway (VPN virtual server, ICA Proxy, CVPN, RDP Proxy) or AAA virtual server as a precondition for the vulnerability.
CVE-2025-3699
Multiple Mitsubishi Electric air conditioners contain an unspecified flaw that may allow a remote attacker to bypass authentication mechanisms and, for instance, take control over the AC system or tamper with firmware. Mitsubishi is preparing patches and recommends immediate mitigation by restricting network and physical access and ensuring systems are updated.
CVE-2025-34046
E-office OA (E-office OA自助平台) contains a flaw in /general/index/UploadFile.php that is triggered as file types and extensions for uploaded files are not properly validated before being placed in a web-accessible path. This may allow a remote attacker to upload, for instance, a file and then request it to execute arbitrary code with the privileges of the web service. An upgrade has been released to mitigate this issue. However, no further details have been provided. As of June 26, this has been reported as being exploited in the wild.
CVE-2025-34036
Shenzhen TVT CCTV-DVR contains a flaw in /language/ that is triggered as input passed via the URI path is not properly sanitized. This may allow a remote attacker to inject and execute arbitrary commands. As of June 23, this has been reported as being exploited in the wild. Flashpoint analysts recommend discontinuing the use of the device, since it is not being supported and no solution exists for this vulnerability.
CVE-2025-34044
The WIFISKY 7-Layer Flow Control Router (WIFISKY 7层流控路由器) contains a flaw in the confirm.php script triggered when input passed via the “t” parameter is not properly validated. This may allow an authenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary OS commands. As of June 26, this has been reported as being exploited in the wild. Flashpoint analysts recommend discontinuing the use of the device since no solution exists for this vulnerability.
Previously Highlighted Vulnerabilities
| CVE/VulnDB ID | Flashpoint Published Date |
| CVE-2025-21218 | Week of January 15, 2025 |
| CVE-2024-57811 | Week of January 15, 2025 |
| CVE-2024-55591 | Week of January 15, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-23006 | Week of January 22, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-20156 | Week of January 22, 2025 |
| CVE-2024-50664 | Week of January 22, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-24085 | Week of January 29, 2025 |
| CVE-2024-40890 | Week of January 29, 2025 |
| CVE-2024-40891 | Week of January 29, 2025 |
| VulnDB ID: 389414 | Week of January 29, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-25181 | Week of February 5, 2025 |
| CVE-2024-40890 | Week of February 5, 2025 |
| CVE-2024-40891 | Week of February 5, 2025 |
| CVE-2024-8266 | Week of February 12, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-0108 | Week of February 12, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-24472 | Week of February 12, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-21355 | Week of February 24, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-26613 | Week of February 24, 2025 |
| CVE-2024-13789 | Week of February 24, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-1539 | Week of February 24, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-27364 | Week of March 3, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-27140 | Week of March 3, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-27135 | Week of March 3, 2025 |
| CVE-2024-8420 | Week of March 3, 2025 |
| CVE-2024-56196 | Week of March 10, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-27554 | Week of March 10, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-22224 | Week of March 10, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-1393 | Week of March 10, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-24201 | Week of March 17, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-27363 | Week of March 17, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-2000 | Week of March 17, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-27636 CVE-2025-29891 | Week of March 17, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-1496 | Week of March 24, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-27781 | Week of March 24, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-29913 | Week of March 24, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-2746 | Week of March 24, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-29927 | Week of March 24, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-1974 CVE-2025-2787 | Week of March 31, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-30259 | Week of March 31, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-2783 | Week of March 31, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-30216 | Week of March 31, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-22457 | Week of April 2, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-2071 | Week of April 2, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-30356 | Week of April 2, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-3015 | Week of April 2, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-31129 | Week of April 2, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-3248 | Week of April 7, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-27797 | Week of April 7, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-27690 | Week of April 7, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-32375 | Week of April 7, 2025 |
| VulnDB ID: 398725 | Week of April 7, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-32433 | Week of April 12, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-1980 | Week of April 12, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-32068 | Week of April 12, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-31201 | Week of April 12, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-3495 | Week of April 12, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-31324 | Week of April 17, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-42599 | Week of April 17, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-32445 | Week of April 17, 2025 |
| VulnDB ID: 400516 | Week of April 17, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-22372 | Week of April 17, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-32432 | Week of April 29, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-24522 | Week of April 29, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-46348 | Week of April 29, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-43858 | Week of April 29, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-32444 | Week of April 29, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-20188 | Week of May 3, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-29972 | Week of May 3, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-32819 | Week of May 3, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-27007 | Week of May 3, 2025 |
| VulnDB ID: 402907 | Week of May 3, 2025 |
| VulnDB ID: 405228 | Week of May 17, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-47277 | Week of May 17, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-34027 | Week of May 17, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-47646 | Week of May 17, 2025 |
| VulnDB ID: 405269 | Week of May 17, 2025 |
| VulnDB ID: 406046 | Week of May 19, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-48926 | Week of May 19, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-47282 | Week of May 19, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-48054 | Week of May 19, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-41651 | Week of May 19, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-20289 | Week of June 3, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-5597 | Week of June 3, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-20674 | Week of June 3, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-5622 | Week of June 3, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-5419 | Week of June 3, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-33053 | Week of June 7, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-5353 | Week of June 7, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-22455 | Week of June 7, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-43200 | Week of June 7, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-27819 | Week of June 7, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-49132 | Week of June 13, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-49136 | Week of June 13, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-50201 | Week of June 13, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-49125 | Week of June 13, 2025 |
| CVE-2025-24288 | Week of June 13, 2025 |
Transform Vulnerability Management with Flashpoint
Request a demo today to see how Flashpoint can transform your vulnerability intelligence, vulnerability management, and exposure identification program.



